
For the last few years the technology of synthesis of synthetic diamonds and techniques of change of diamonds properties, mainly on the improvement of color group have stepped far forward. At present СVD and HPHT technologies allow growing synthetic diamonds weighing more than 10 carats, and diagnostics of diamond origin is becoming more complicated and high-tech. The same is with treated diamonds.
Diamonds color can be modified not for all precious stones, but exclusively for type IIa natural diamonds (according to physical classification of diamonds).
Today in the domestic jewelry market, more and more common are synthetic cut diamonds and treated diamonds. And while in the USA they are quite legal independent trends (natural diamonds, treated natural diamonds, synthetic cut diamonds), in Russia, in most cases, the producer hides the nature of the origin of precious stones, though their value significantly differs from the natural analogues not exposed to external actions.
Diamonds diagnostics
Visually treated diamonds and synthetic cut diamonds do not differ from their natural analogues. They are also identical in their physical and chemical properties. Moreover, the so-called diamond-testers, systems of “CLIO-TESTER” and “DUO-TESTER” type, mostly often found in jewelry stores, identify them as diamonds.
To diagnose traces of artificial synthesis and external action for improving the color is possible exclusively with the help of extremely expensive modern equipment. The most widespread in Russia, Belgian “D-screen”, unfortunately, also has limited use, mainly due to the following factors:
- its inability to study diamonds in jewelry;
- yellow color of the indicator is not a sign of artificial origin of a diamond or diamond treatment. It only shows that the sample belongs to the so-called nitrogen-free type and needs additional diagnosis.
Yellow “D-screen” indicator
World gemological practice shows that methods of diagnostics based on the spectroscopic study of samples are the most versatile. But they are quite expensive (mainly because of the cost of the equipment); require highly skilled personnel, the use of liquid nitrogen, etc. Therefore, such certification laboratories as GIA (Gemological Institute of America), Smolensk Gemological Center, give preference to equipment, developed by De Beers Company, - a complex of “Diamond View” and “Diamond Sure” systems. At sufficiently high cost these systems are convenient and reliable in use and with high accuracy can diagnose synthetic diamonds and treated diamonds.
“Diamond Sure” System
“Diamond Sure” which principle of operation is similar to «D-screen», allows to study fixed in the item diamonds, and in case of labeling the studied sample as IIa type, indicates which additional studies are to be performed. Besides, in the “Diamond Sure” the range of ordinary colors of the diamonds under study is extended to 8-4 (“D-screen” only up to color group 7).
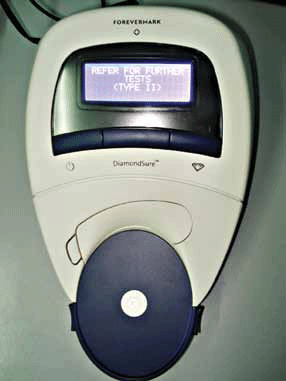
“Diamond Sure” Device
“Diamond View” System
“Diamond View” combines the functions of a source of short-wave ultraviolet radiation and an electronic microscope with high magnification and allows diagnosing diamonds and synthetic cut diamonds of ordinary and fancy colors. By certain characteristic features of the shortwave UV luminescence the sample under study can be attributed to one or another group (see figures).

“Diamond View” Device
Diamonds
Characteristic Features
1. Uniform blue SW-luminescence (SW - short-wave, is excited by the ultraviolet).
2. Structural areas have the form of irregular figures and are not bitterly (in other color) marked out on the general SW luminescence background.

Diamonds subjected to HPHT-effect (high pressure and temperature) for the purpose of changing color.
Characteristic Features
1. Colored yellow structural lines on the general background of SW-blue luminescence.
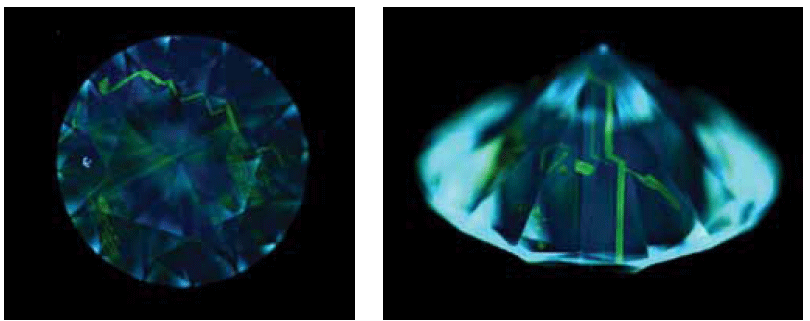
Synthetic cut diamonds (HPHT method of synthesis)
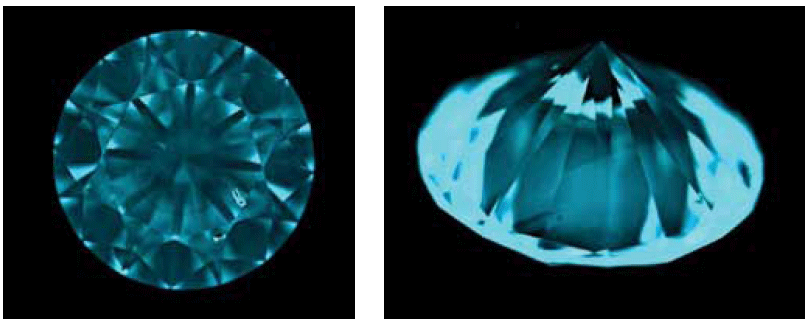
Characteristic Features
1. White-blue, with grayish toning SW-luminescence.
2. Dislocation lines and areas, visible through the pavilion at the SW-luminescence.
Diamonds diagnostics concerning natural/artificial origin, traces of color change and/or clarity is rather a complex process requiring the use of expensive and complicated equipment, availability of a constantly updated database of the characteristic features of treated diamonds and synthetic cut diamonds and, most importantly, qualified experts.
Recommendations for a consumer when buying diamonds and diamond jewelry:
1. Pay attention to the diamond girdle. The presence of laser marking “GE POL”, “HPHT PROCESSED” testifies that you have a treated diamond or a synthetic cut diamond in front of you.
2. Demand the certificate on the diamond. Pay attention to the diamond certificate, not the jewelry’s label. At that, make the difference between the diamond certificate and the synthetic cut diamond certificate. According to world gemological practice they differ even in color (a synthetic cut diamond certificate is usually yellow).
Even in case when you have a diamond certificate in front of you, pay attention to the item “Presence of signs of external action aiming at color and/or clarity change”. Unfortunately, in domestic practice of certification of diamonds out of 10 certification laboratories only Smolensk Gemological Center has an approved form of synthetic cut diamond conformity certificate and corresponding registered standard. Moreover, in most certificates of other gemological laboratories the item “Presence of signs of external action aiming at color and/or clarity change” is absent: that is, a natural diamond without any external action and a treated diamond have identical certificates.
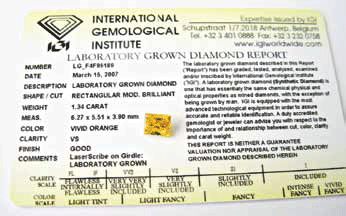
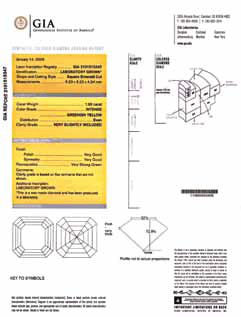
Conformity certificates of synthetic cut diamonds of IGI and GIA foreign certification centers
4. Buy diamonds and jewelry only from proven manufacturers, reputable in the market. So, for example, the purchase of diamond raw material by JSC “MO Crystal” from such companies as “ALROSA” and De Beers introduces a number of restrictions into the activity of the enterprise: neither synthesize, treat nor make researches of, including marketing, synthetic cut diamonds and treated diamonds.
Author: Denis Slabkovsky, General Director of LLC “Smolensk Gemological Center

